Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
(Tag: Visual edit) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<!-- TODAY'S FEATURED ARTICLE --> | <!-- TODAY'S FEATURED ARTICLE --> | ||
| id="mp-left" class="MainPageBG" style="width:55%; padding:0; vertical-align:top; color:#000;" | | | id="mp-left" class="MainPageBG" style="width:55%; padding:0; vertical-align:top; color:#000;" | | ||
| − | <h2 id="mp-tfa-h2" style="margin:0.5em; background:#cef2e0; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Featured article: PFAS | + | <h2 id="mp-tfa-h2" style="margin:0.5em; background:#cef2e0; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Featured article: PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) and PFAS Enhanced Retention (PER)</h2> |
| − | <div id="mp-tfa" style="padding:0.0em 1.0em;">[[File: | + | <div id="mp-tfa" style="padding:0.0em 1.0em;">[[File:AdamsonFig2.png|500px|left|link=PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) and PFAS Enhanced Retention (PER)]]<dailyfeaturedpage></dailyfeaturedpage> |
| − | [[PFAS | + | |
| + | [[PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) and PFAS Enhanced Retention (PER)|(Full article...)]] </div> | ||
| style="border:1px solid transparent;" | | | style="border:1px solid transparent;" | | ||
| Line 87: | Line 88: | ||
*[[Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)|Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)]] | *[[Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)|Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)]] | ||
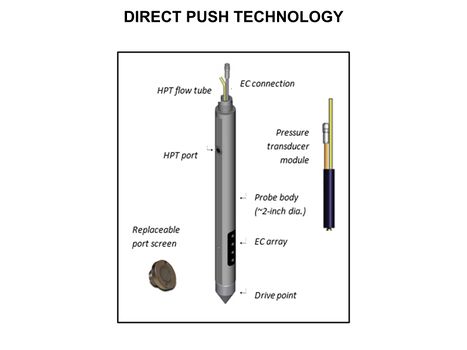
*[[Direct Push (DP) Technology]] | *[[Direct Push (DP) Technology]] | ||
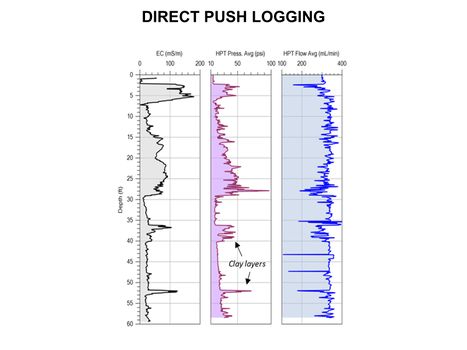
| − | **[[Direct Push Logging | Direct Push Logging]] | + | **[[Direct Push Logging |Direct Push Logging]] |
| − | **[[Direct Push Sampling | Direct Push Sampling]] | + | **[[Direct Push Sampling |Direct Push Sampling]] |
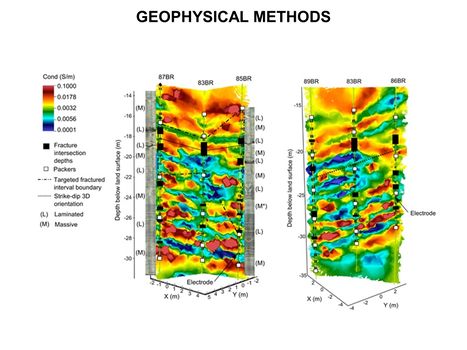
*[[Geophysical Methods | Geophysical Methods]] | *[[Geophysical Methods | Geophysical Methods]] | ||
| − | **[[Geophysical Methods - Case Studies | Case Studies]] | + | **[[Geophysical Methods - Case Studies |Case Studies]] |
| + | **[[Hydrogeophysical Methods for Characterization and Monitoring of Groundwater-Surface Water Exchanges]] | ||
*[[Groundwater Sampling - No-Purge/Passive]] | *[[Groundwater Sampling - No-Purge/Passive]] | ||
*[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)|Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)]] | *[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)|Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)]] | ||
| − | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Analysis | LTM Data Analysis]] | + | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Analysis |LTM Data Analysis]] |
| − | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Variability | LTM Data Variability]] | + | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Variability |LTM Data Variability]] |
| − | *[[Molecular Biological Tools - MBTs | Molecular Biological Tools (MBTs)]] | + | *[[Molecular Biological Tools - MBTs |Molecular Biological Tools (MBTs)]] |
**[[Metagenomics]] | **[[Metagenomics]] | ||
**[[Proteomics and Proteogenomics]] | **[[Proteomics and Proteogenomics]] | ||
**[[Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)]] | **[[Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)]] | ||
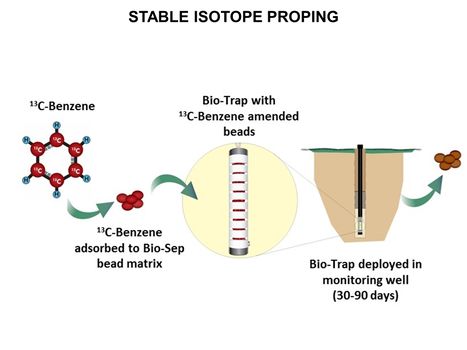
**[[Stable Isotope Probing (SIP)]] | **[[Stable Isotope Probing (SIP)]] | ||
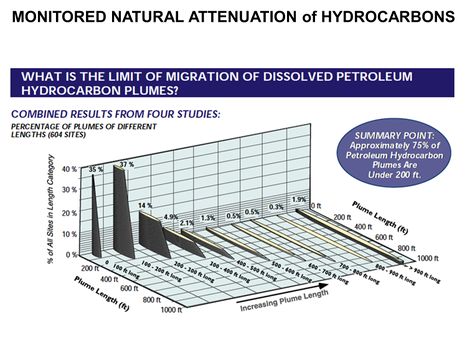
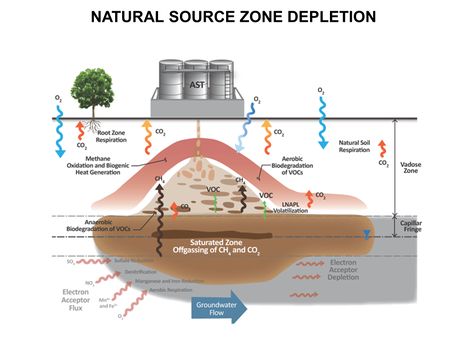
| − | *[[Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume - Bemidji Crude Oil Spill | Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume -<br /> Bemidji Crude Oil Spill]] | + | *[[Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume - Bemidji Crude Oil Spill |Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume -<br />Bemidji Crude Oil Spill]] |
*[[OPTically-based In-situ Characterization System (OPTICS)]] | *[[OPTically-based In-situ Characterization System (OPTICS)]] | ||
| Line 133: | Line 135: | ||
<u>'''[[Munitions Constituents]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Munitions Constituents]]'''</u> | ||
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Abiotic Reduction| Abiotic Reduction]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Abiotic Reduction|Abiotic Reduction]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Alkaline Degradation| Alkaline Degradation]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Alkaline Degradation|Alkaline Degradation]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Composting| Composting]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Composting|Composting]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Deposition | Deposition]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Deposition |Deposition]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Dissolution | Dissolution]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Dissolution |Dissolution]] |
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Electrochemical Treatment|Electrochemical Treatment]] | ||
*[[Metal(loid)s - Small Arms Ranges]] | *[[Metal(loid)s - Small Arms Ranges]] | ||
| − | *[[Passive Sampling of Munitions Constituents| Passive Sampling]] | + | *[[Passive Sampling of Munitions Constituents|Passive Sampling]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents – Photolysis | Photolysis]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents – Photolysis |Photolysis]] |
*[[Munitions Constituents – Sample Extraction and Analytical Techniques|Sample Extraction and Analytical Techniques]] | *[[Munitions Constituents – Sample Extraction and Analytical Techniques|Sample Extraction and Analytical Techniques]] | ||
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Soil Sampling | Soil Sampling]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Soil Sampling |Soil Sampling]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Sorption | Sorption]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Sorption |Sorption]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - IM Toxicology | Toxicology]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - IM Toxicology |Toxicology]] |
*[[Munitions Constituents- TREECS™ Fate and Risk Modeling|TREECS™]] | *[[Munitions Constituents- TREECS™ Fate and Risk Modeling|TREECS™]] | ||
| Line 159: | Line 162: | ||
*[[PFAS Ex Situ Water Treatment]] | *[[PFAS Ex Situ Water Treatment]] | ||
**[[PFAS Treatment by Anion Exchange]] | **[[PFAS Treatment by Anion Exchange]] | ||
| + | *[[PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) and PFAS Enhanced Retention (PER)]] | ||
*[[PFAS Soil Remediation Technologies]] | *[[PFAS Soil Remediation Technologies]] | ||
*[[PFAS Sources]] | *[[PFAS Sources]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:15, 4 March 2025
Peer Reviewed. Accessible. Written By Experts |
Your Environmental Information Gateway |
| The goal of ENVIRO Wiki is to make scientific and engineering research results more accessible to environmental professionals, facilitating the permitting, design and implementation of environmental projects. Articles are written and edited by invited experts (see Contributors) to summarize current knowledge for the target audience on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. | See Table of Contents |
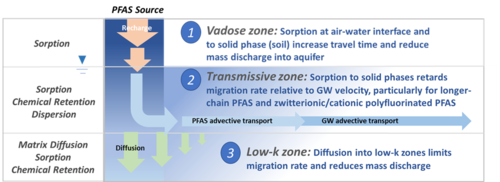
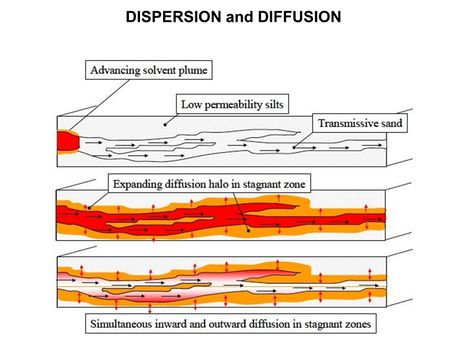
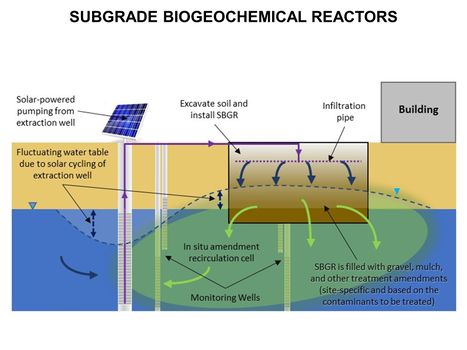
Featured article: PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) and PFAS Enhanced Retention (PER)Groundwater sites contaminated with PFAS are difficult to investigate and remediate due to strict cleanup goals, lack of natural degradation mechanisms for some PFAS, and the high mobility and persistence of several PFAS. As a result, understanding and potentially relying on processes that reduce PFAS migration rates and mass discharge rates is of considerable interest to site managers. This includes a variety of chemical and geochemical retention processes that have been incorporated into the PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) approach. PMR is a similar concept to monitored natural attenuation (MNA), and the term has recently been adopted in place of MNA to avoid potential confusion with destructive and/or permanent attenuation processes that are part of the MNA strategies for other constituents of concern (COCs). However, many of the processes remain the same, and they are expected to reduce PFAS concentrations and mass discharge during transport from source areas. A key concept of PMR is that retention processes can provide a credible scientific basis for attenuation of PFAS concentrations or mass discharge over time (or distance) that reduce the mobility and risk associated with PFAS in the subsurface. PMR may have applicability as a sole remedy at low-risk sites, but it could also help control low levels of remaining contamination after active treatment. It may also serve as a temporary remedy at sites with no proximate receptors, giving time for the development of more cost-effective technologies. Finally, it can be part of a treatment train at more complex sites where risk-based approaches are acceptable.
(Full article...)
|
Enviro Wiki Highlights |